What is thyroid and its importance
The thyroid gland is part of the endocrine system and develops and delivers thyroid hormones into the blood flow. The thyroid gland is at the front line of the neck just below the larynx. It is a butterfly-shaped and comprises two lobes situated either side with the trachea. The thyroid gland provides hormones that govern the body’s metabolic rate, heart, digestive function, muscle control, brain development, mood, and bone preservation. Its correct function depends on having a healthy supply of iodine from the diet.
The thyroid makes several hormones, of which two are significant ones and triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones help oxygen grow into cells and create your thyroid as an important gland of metabolism. Many pathologists observe that all the hormones generated by the thyroid, 80 percent will be T4 and 20 percent T3. After development, T3 and T4 travel through the bloodstream. The primary purpose is to promote cells that convert oxygen and calories into energy. The hypothalamus in the brain releases Thyrotropin-releasing Hormone (TRH). The release of TRH allows the pituitary gland to release Thyroid-Stimulating hormone (TSH). This TSH also allows the thyroid to produce thyroid hormones that release them into your blood flow.
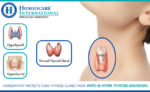
Thyroid hormones are the mediators of many chemical reactions within the body. The thyroid gland, because of its unique action it becomes a regulator of the rate at which the body functions. The thyroid gland provides thyroxine and calcitonin. Calcitonin plays an important role in controlling calcium levels in the body. The thyroid gland can become overactive (hyperthyroidism) or underactive (hypothyroidism) that depends on T3 and T4 levels. The enlargement of the thyroid gland kenned as goiter. Thyrotoxicosis is the term given when there is an excess amount of thyroid hormone in the bloodstream. It may result from overactivity of the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism) as in Graves’ disease, inflammation of the thyroid or a weak thyroid tumour.
What is thyroid dysfunction?
The thyroid gland develops hormones that coordinate your body’s metabolism. Several complications can emerge when your thyroid generates very much hormone (hyperthyroidism) or not sufficient (hypothyroidism). Four prevalent complications from the thyroid are Hashimoto’s disease, Graves’ disease, goiter, and thyroid nodules.
Signs and symptoms of thyroid dysfunction
Symptoms of the thyroid dysfunction include intolerance to hot weather, weight loss, increased appetite, gained bowel movements, inappropriate menstrual cycle, speedy and irregular heartbeat, palpitations, fatigue, irritation, tremor, hair loss and retraction of the eyelids following in a ‘staring’ appearance. Other signs and symptoms of thyroid dysfunction include increased sensitivity to cold and heat, constipation, dry skin, weight gain, puffy face, muscle weakness, and hoarse.
Thyroid Treatment in Homeopathy
Homeopathy treatment for Thyroid dysfunction is very effective in treating Thyroid disorders and its symptoms. Thyroid treatment in homeopathy involves regulating thyroid gland functioning and balance hormonal secretion.
Expert Homeopathy Doctors at Homeocare International provide constitutional homeopathy treatment for thyroid dysfunction . Thyroid treatment in homeopathy is based on the symptoms, previous health history of the individual and individualization. Constitutional homeopathy treatment for Thyroid dysfunction is safe, effective and not just focuses on thyroid disorders but also treats the root cause of the problem.
To know more about Homeopathy Treatment for Hyperthyroidism at Homeocare International, Please call 1800-102-2202 or visit https://www.homeocare.in/thyroid-treatment.html
Author Bio: Dr.Ambika B, BHMS is a Homeopathy Expert having 12 years of Experience in the field of Homeopathy, serving at Homeocare international Miyapur branch, Hyderabad, Telangana.